This paper studies close-loop task planning, which refers to the process of generating a sequence of skills (a plan) to accomplish a specific goal while adapting the plan based on real-time observations.
Recently, prompting Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate actions iteratively has become a prevalent paradigm due to its superior performance and user-friendliness.
However, this paradigm is plagued by two inefficiencies: high token consumption and redundant error correction, both of which hinder its scalability for large-scale testing and applications.
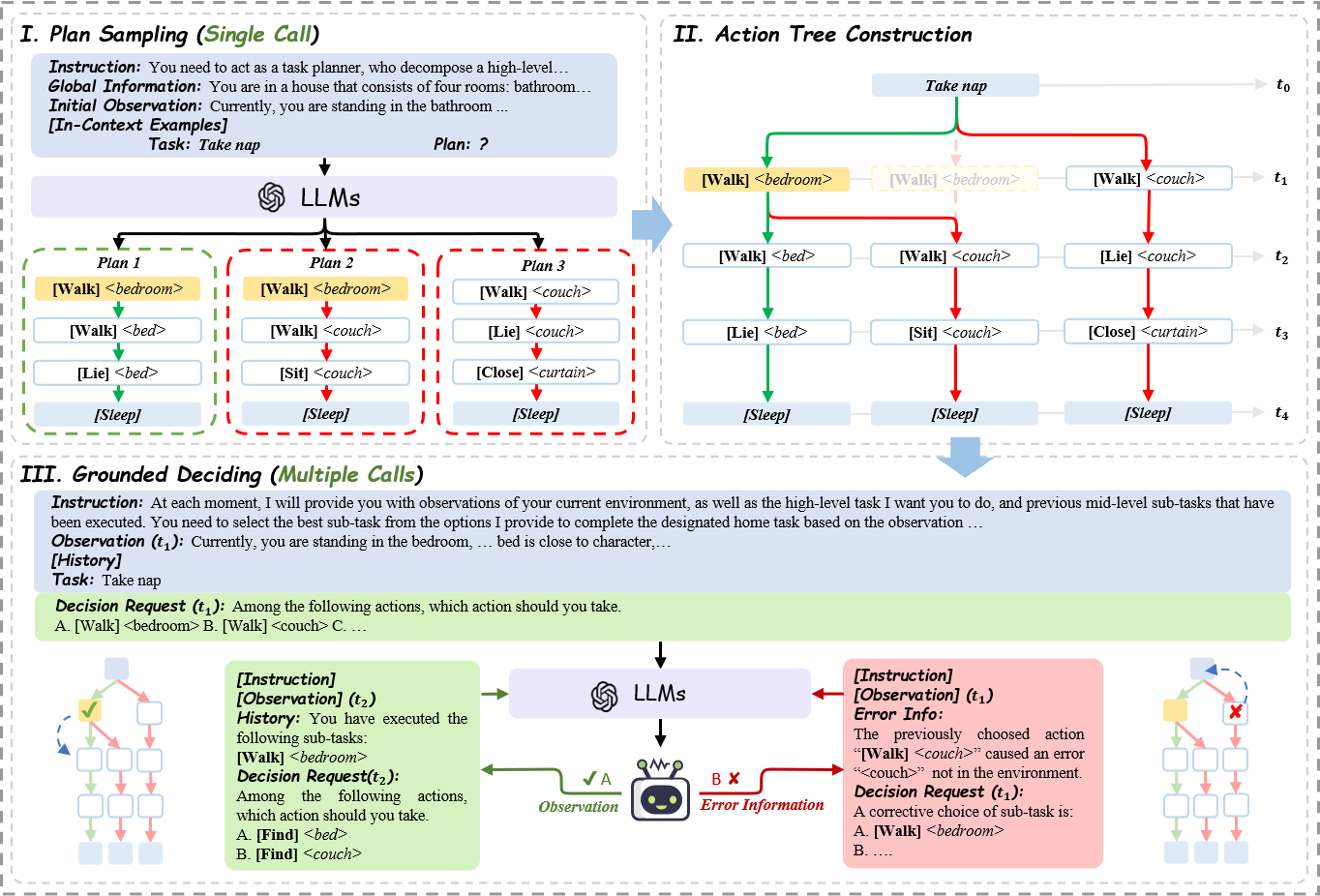
To address these issues, we propose Tree-Planner, which reframes task planning with LLMs into three distinct phases:
plan sampling, action tree construction, and grounded deciding.
Tree-Planner starts by using an LLM to sample a set of potential plans before execution, followed by the aggregation of them to form an action tree.
Finally, the LLM performs a top-down decision-making process on the tree, taking into account real-time environmental information.
Experiments show that Tree-Planner achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining high efficiency.
By decomposing LLM queries into a single plan-sampling call and multiple grounded-deciding calls,
a considerable part
of the prompt are less likely to be repeatedly consumed.
As a result, token consumption is reduced by 92.2% compared to the previously best-performing model.
Additionally, by enabling backtracking on the action tree as needed, the correction process becomes more flexible, leading to a 40.5% decrease in error corrections.